> hospital Tepic
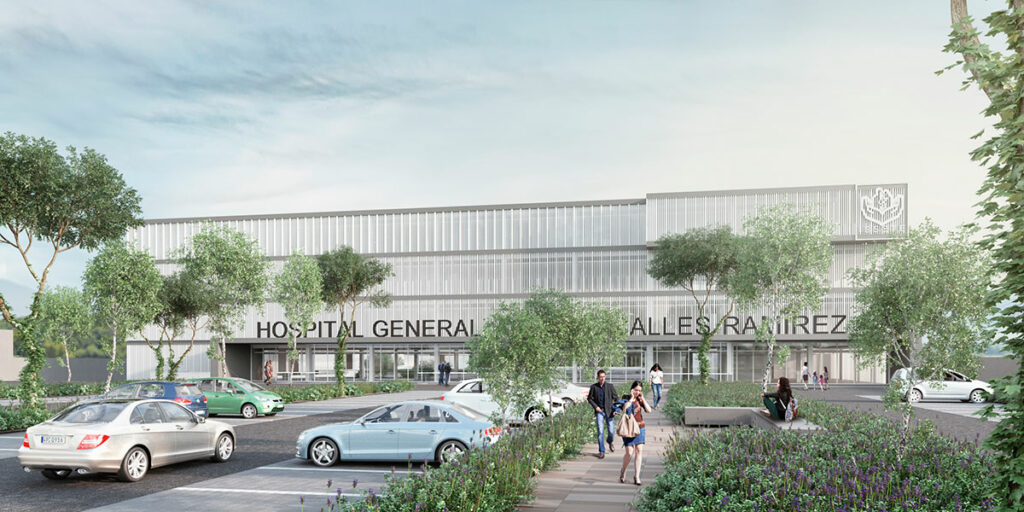
The property is located in the "La Cantera" ejido, 8 minutes from the municipal center of Tepic, and has a surface area of 35,000 m².
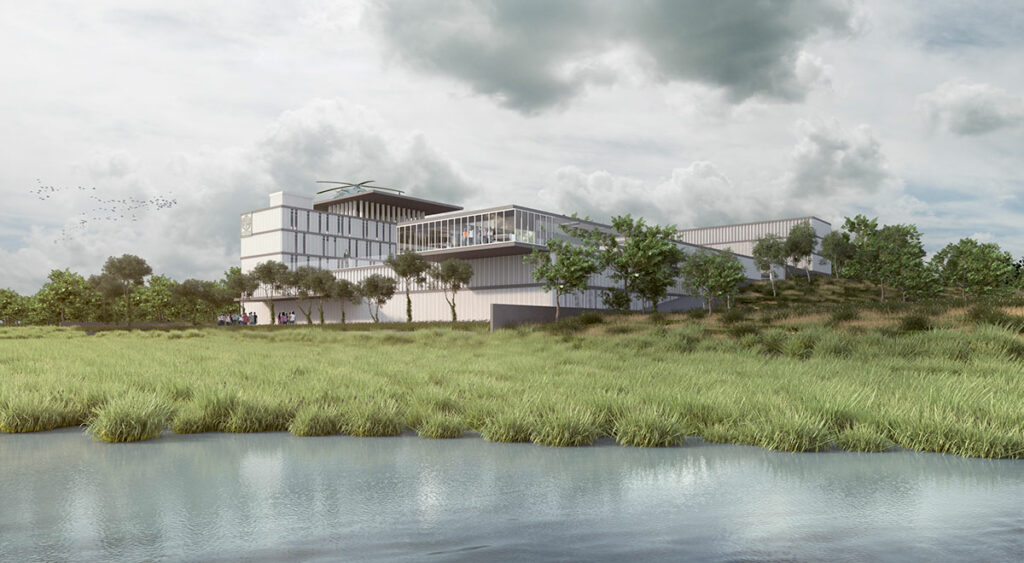
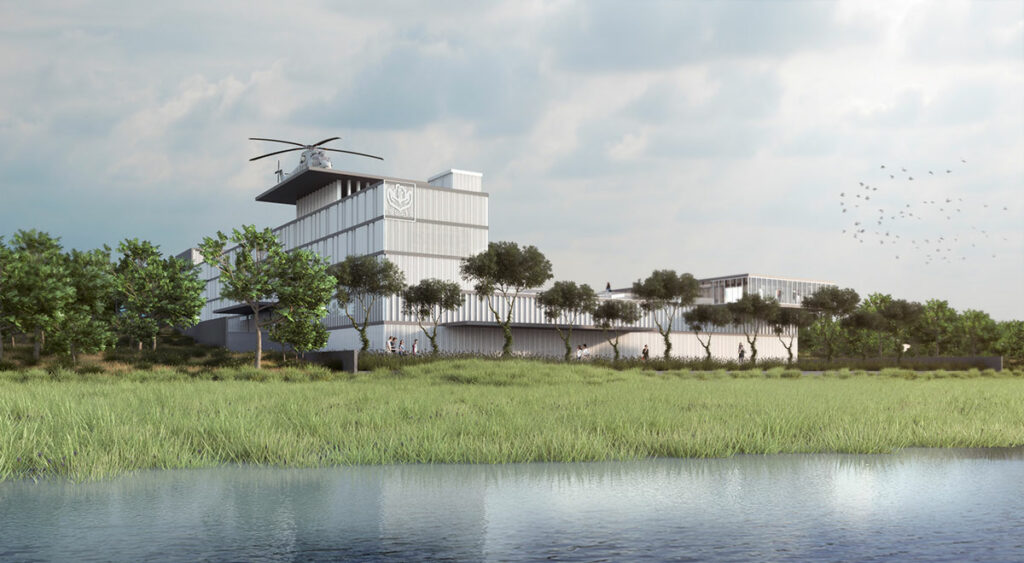
The land features a significant slope, and its subsoil consists mostly of fine, soft soils and clays, with a shallow water table approximately 3.30 meters deep.
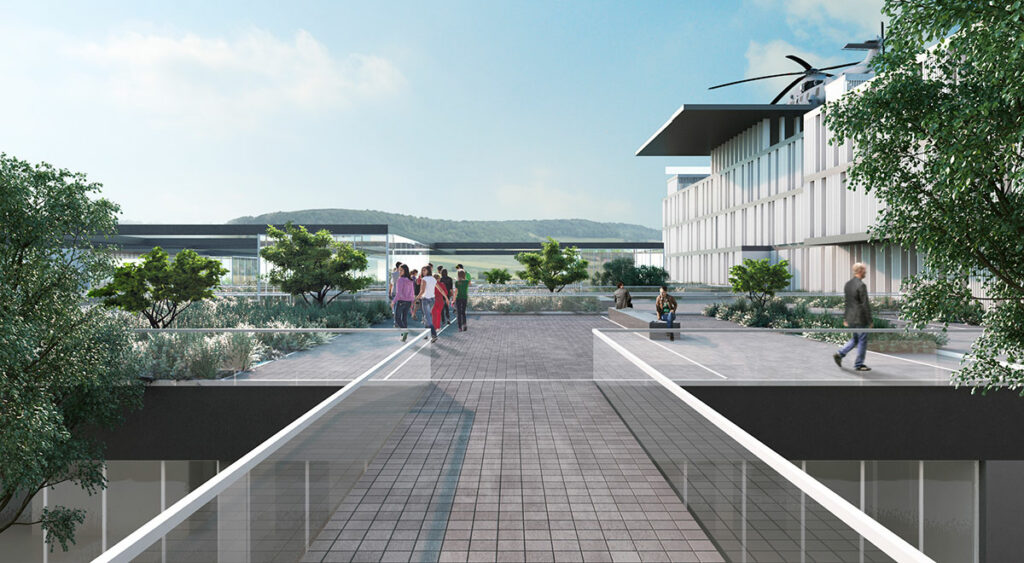
The hospital design, developed in collaboration with Estudio Lamela and Villar Watty Arquitectos, is based on strict criteria of functionality and organization, grouping different services according to their purpose and maintaining separate circulation paths to avoid undesired crossings between different hospital users.
This design enhances comfort for both patients and staff, while allowing flexibility for future expansion of the building without affecting its operations.
Several technological and ecological innovations are included to ensure the building's sustainable performance.
Passive eco-technologies include proper building orientation, the use of local and thermal materials, green roofs, and rainwater collection systems for irrigation.
Active eco-technologies include solar panels for parking lot lighting, solar water heaters, wind energy generators, and electric vehicle charging stations.
The hospital's medical-architectural program includes medical care areas with 150 beds, outpatient services, specialty medical care, and various consulting rooms.
The building’s structure is designed with telecommunications, electrical and lighting systems, as well as hydraulic, sanitary, rainwater drainage, fire protection, irrigation, LP gas and diesel systems, and medical gas systems.


The property is located in the "La Cantera" ejido, 8 minutes from the municipal center of Tepic, and has a surface area of 35,000 m².
The land features a significant slope, and its subsoil consists mostly of fine, soft soils and clays, with a shallow water table approximately 3.30 meters deep.
The hospital design, developed in collaboration with Estudio Lamela and Villar Watty Arquitectos, is based on strict criteria of functionality and organization, grouping different services according to their purpose and maintaining separate circulation paths to avoid undesired crossings between different hospital users.
This design enhances comfort for both patients and staff, while allowing flexibility for future expansion of the building without affecting its operations.
Several technological and ecological innovations are included to ensure the building's sustainable performance.
Passive eco-technologies include proper building orientation, the use of local and thermal materials, green roofs, and rainwater collection systems for irrigation.
Active eco-technologies include solar panels for parking lot lighting, solar water heaters, wind energy generators, and electric vehicle charging stations.
The hospital's medical-architectural program includes medical care areas with 150 beds, outpatient services, specialty medical care, and various consulting rooms.
The building’s structure is designed with telecommunications, electrical and lighting systems, as well as hydraulic, sanitary, rainwater drainage, fire protection, irrigation, LP gas and diesel systems, and medical gas systems.